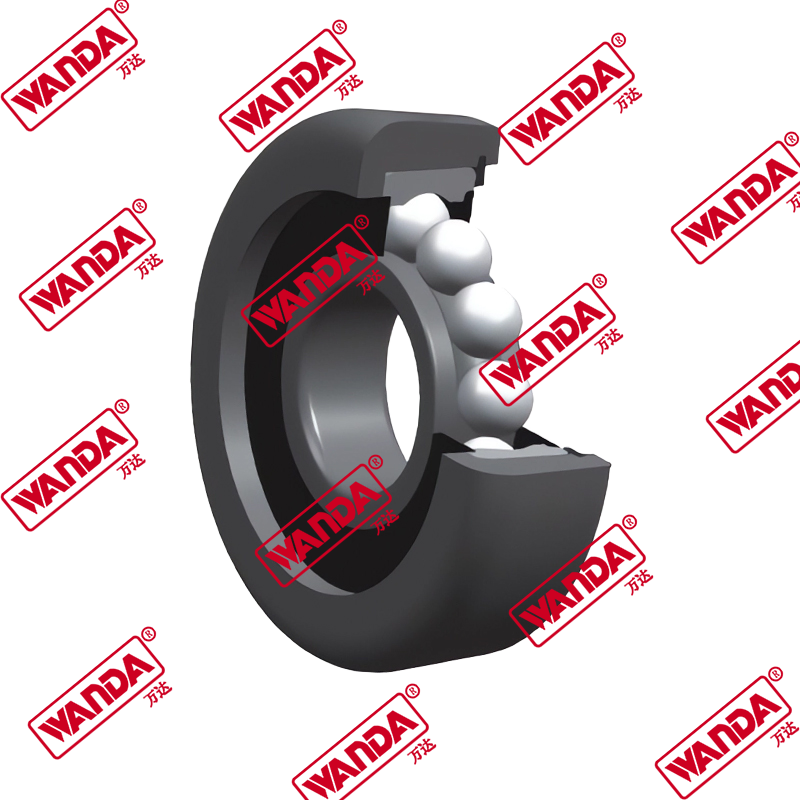
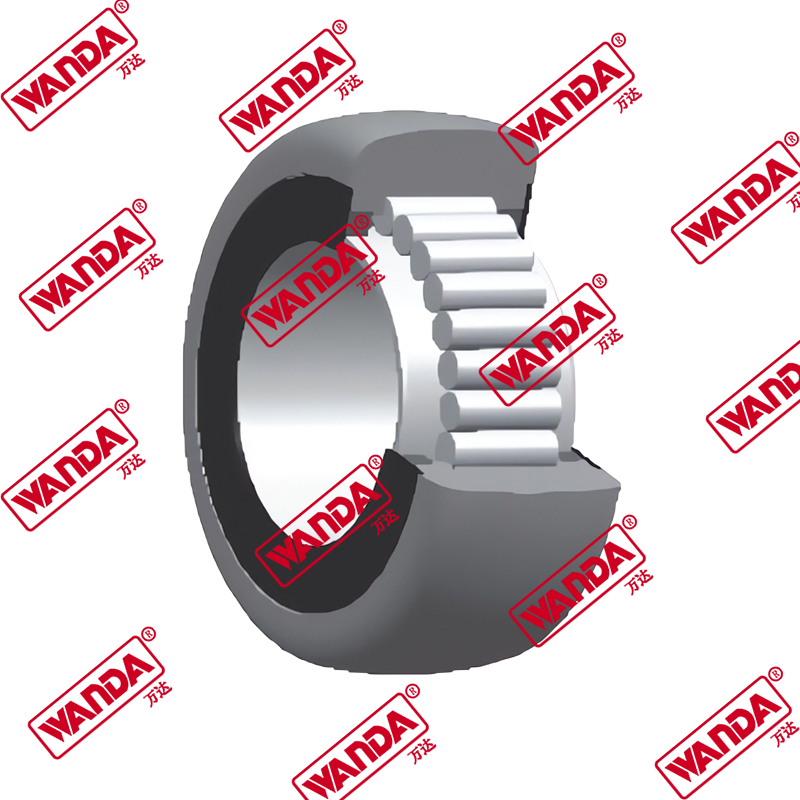
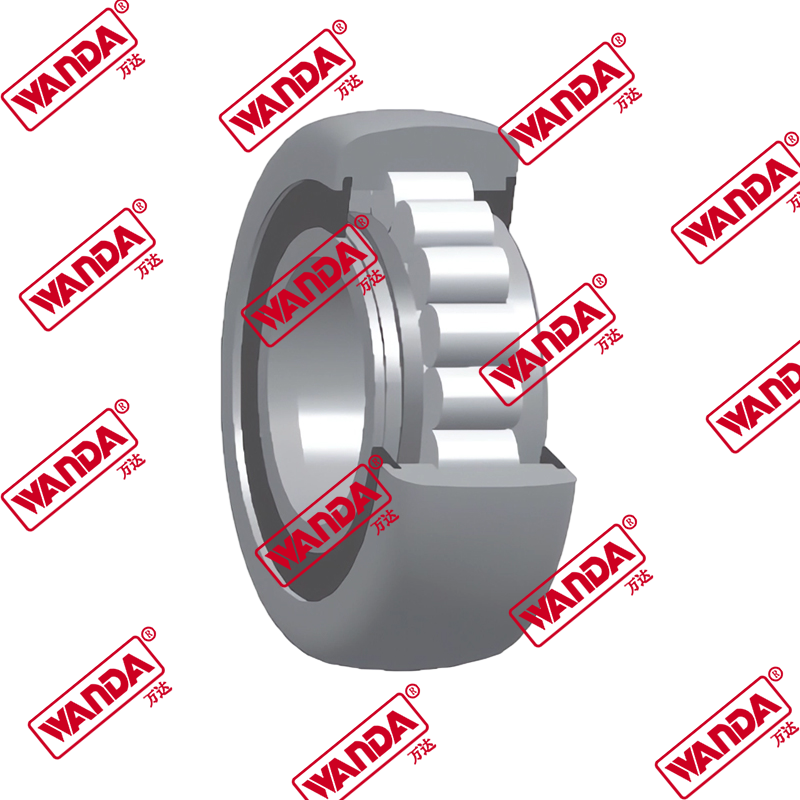
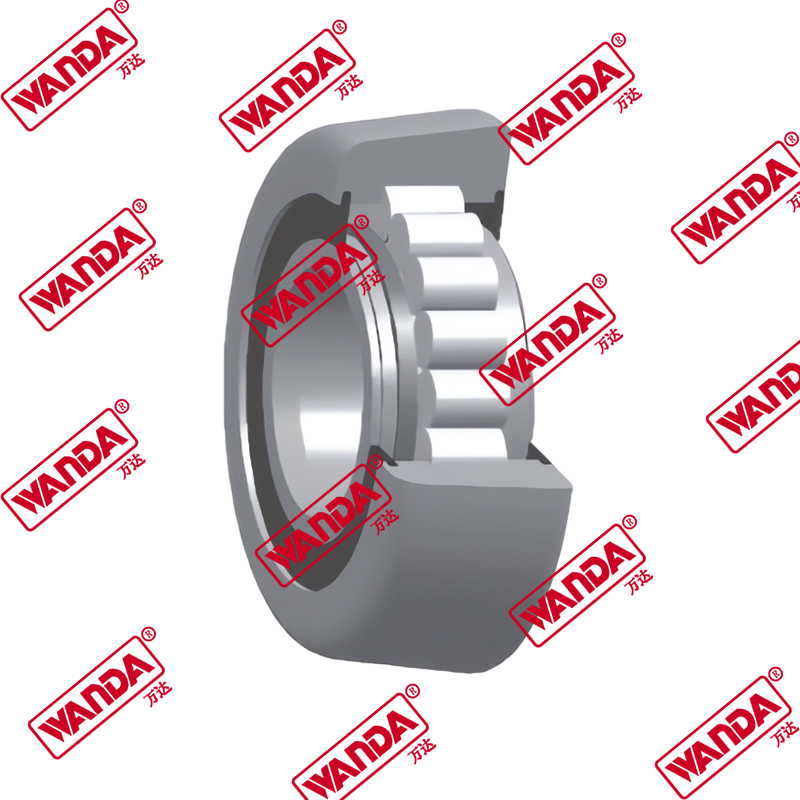
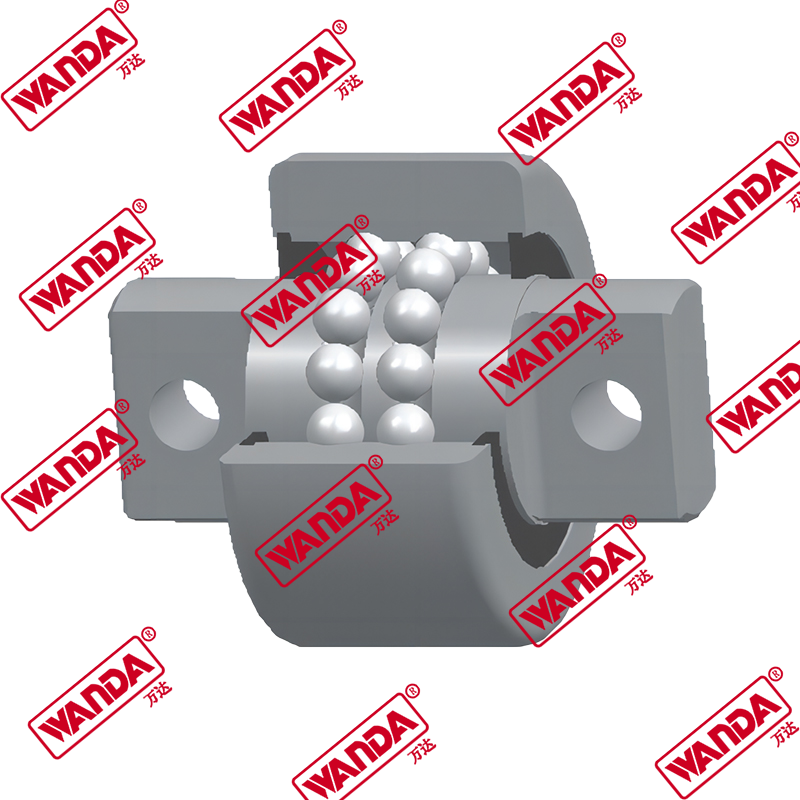
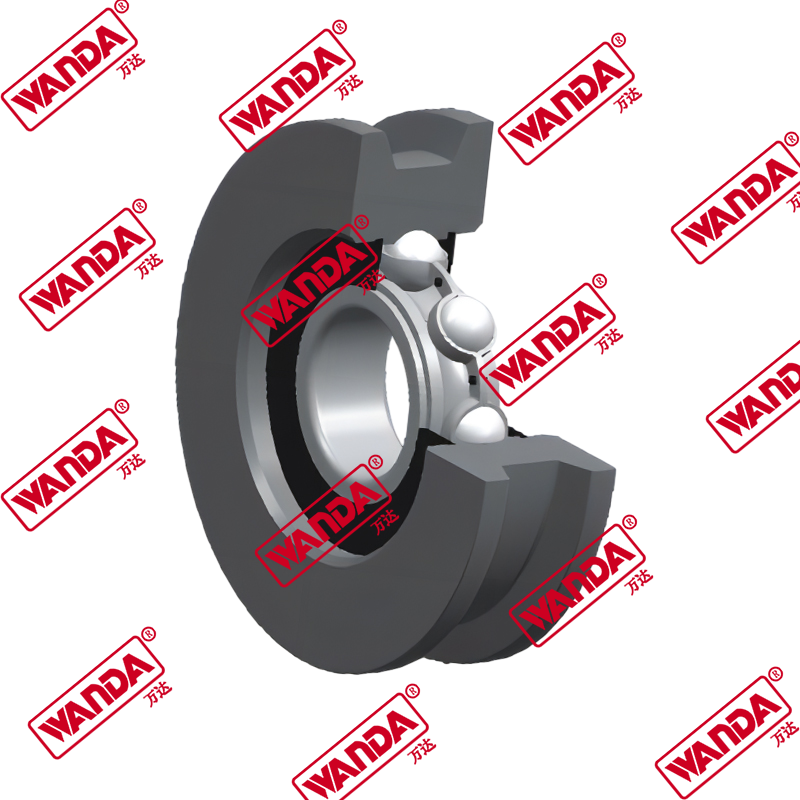
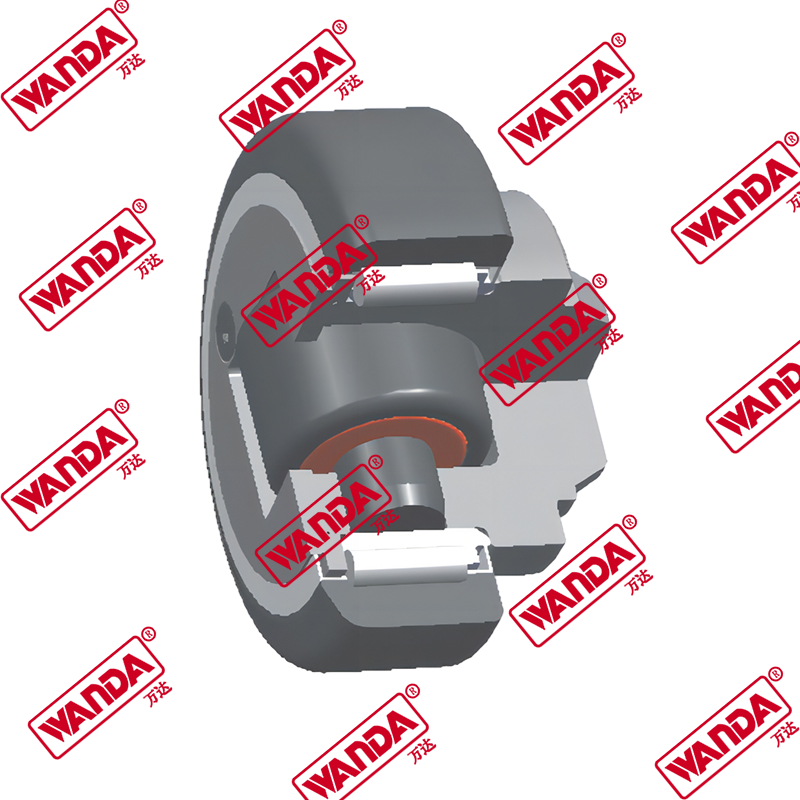
In the material handling industry, the structural integrity and smooth operation of a lifting system rely heavily on precision components. The Forklift Mast Guide Bearing is a specialized heavy-duty roller designed to withstand high radial and axial loads while facilitating the vertical movement of the mast stages. Unlike standard industrial bearings, these components must endure eccentric loading and harsh environmental debris. Understanding the mechanical nuances of a Forklift Mast Guide Bearing is essential for fleet engineers and maintenance managers aiming to minimize downtime and ensure operator safety.
1. Mechanical Function and Structural Design
A Forklift Mast Guide Bearing (also known as a forklift mast roller) acts as the interface between the fixed and telescopic mast channels. Its primary engineering function is to reduce friction while maintaining the alignment of the mast under full capacity. Due to the nature of cantilevered loads, these bearings experience significant moment loads. High-quality rollers feature thick-walled outer rings to resist deformation and specialized internal geometries to handle side thrust. When comparing different mast architectures, the choice of bearing depends on the clearance between the channels and the required lifting speed.
Comparison: Standard Deep Groove vs. Forklift Mast Bearings
While standard bearings focus on high-speed rotation, mast guide bearings are engineered for high static load capacity and impact resistance.
| Feature | Standard Deep Groove Bearing | Forklift Mast Guide Bearing |
| Outer Ring Wall Thickness | Thin (Optimized for weight) | Extra-Thick (Optimized for rail contact) |
| Load Type Support | Primarily Radial | Radial + Heavy Axial/Side Thrust |
| Internal Clearance | C3 Standard | Tight Tolerances for Mast Stability |
2. Identifying Signs of Wear and Failure
Engineers must be vigilant regarding symptoms of worn forklift mast bearings. Common indicators include uneven mast tracking, audible grinding noises during lifting, and visible "scuffing" on the mast rails. A critical failure mode is the flattening of the outer ring, which occurs if the bearing seizes or if the forklift is consistently overloaded. If the mast exhibits excessive lateral "play" or wobbling, it is often a sign that the Forklift Mast Guide Bearing has suffered internal raceway fatigue. Regular inspection of the mast rail's wear pattern can provide early warnings before a catastrophic failure occurs.
3. Technical Protocols for Replacement and Adjustment
The process of forklift mast roller replacement requires precision and adherence to manufacturer torque specifications. During replacement, it is not enough to simply swap the bearing; the technician must also inspect the shims and the mast rail condition. Shimming is vital to ensure that the Forklift Mast Guide Bearing maintains contact with the rail without causing excessive binding. If the bearings are too tight, friction increases heat and wear; if too loose, the mast will lose structural rigidity. Proper mast bearing lubrication using high-pressure lithium-based grease is mandatory to flush out contaminants and reduce the friction coefficient.
Comparison: Sealed vs. Shielded Mast Bearings
The choice of sealing determines the bearing's longevity in dusty warehouse environments versus outdoor construction sites.
| Sealing Type | Shielded (ZZ) | Sealed (RS/DDU) |
| Contaminant Protection | Moderate (Blocks large debris) | Superior (Blocks fine dust and moisture) |
| Grease Retention | Good | Excellent |
| Friction Levels | Very Low | Slightly Higher due to Seal Contact |
4. Optimizing Lifespan: Maintenance and Environment
To maximize the forklift mast bearing lifespan, environmental factors must be controlled. In cold storage applications, specialized low-temperature grease must be used to prevent the lubricant from thickening. Conversely, in foundries or heavy manufacturing, heat-resistant seals are necessary. Understanding how to lubricate forklift mast channels correctly ensures that the outer diameter of the Forklift Mast Guide Bearing glides rather than slides, preventing the common "flat spot" issue. Furthermore, choosing the best grease for forklift mast rollers involves selecting a lubricant with high "tackiness" that won't drip off the vertical rails during operation.
Key Maintenance Checkpoints:
- Inspect outer ring for cracks or pitting.
- Check for seal integrity and grease leakage.
- Measure the forklift mast roller dimensions to detect significant wear.
- Verify shim thickness to maintain mast alignment.
5. Sourcing and Selection Criteria
When selecting a replacement, it is crucial to match the forklift mast guide bearing specifications exactly to the original equipment manufacturer's requirements. Variations in the outer diameter or the width of the bearing by even 1mm can lead to improper tracking and accelerated rail wear. Engineers often debate heavy duty vs standard mast rollers; however, the decision should always be based on the duty cycle of the machine. For 24/7 high-intensity operations, investing in premium-grade rollers with optimized heat treatment is the most cost-effective strategy long-term.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. How often should I perform mast bearing lubrication?
Lubrication frequency depends on the environment. In standard warehouse conditions, every 250 operating hours is typical. In dusty or outdoor environments, this should be reduced to every 50-100 hours to prevent abrasive paste formation.
2. Can I replace just one Forklift Mast Guide Bearing at a time?
While possible, it is highly recommended to replace mast bearings in pairs (left and right) for a specific stage. This ensures balanced load distribution and prevents the new bearing from being prematurely worn by an older, misaligned counterpart.
3. What are the most common symptoms of worn forklift mast bearings?
The most common symptoms include a "jerking" motion when the mast is lowered, visible metal shavings in the mast channels, and the mast leaning to one side when under load.
4. Does forklift mast roller replacement require a specialized press?
In many cases, yes. These bearings are press-fitted onto the carriage pins. Using improper tools like hammers can damage the internal raceways of the new bearing before it is even put into service.
5. Why is the forklift mast bearing lifespan shorter on electric forklifts in cold storage?
Cold storage causes condensation when the machine exits the freezer. This moisture can bypass inferior seals, leading to internal corrosion and grease washout, which significantly shortens the component's life.
Industry References
- ISO 22915: Industrial trucks — Verification of stability.
- ABMA Standard 7: Shaft and Housing Fits for Metric Radial Ball and Roller Bearings.
- ANSI/ITSDF B56.1: Safety Standard for Low Lift and High Lift Trucks.