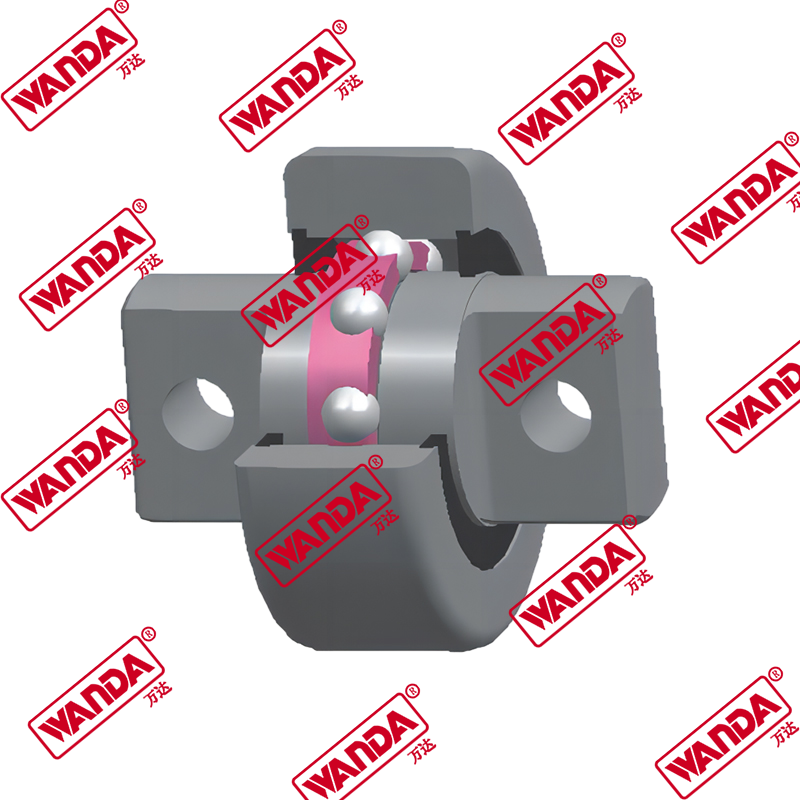
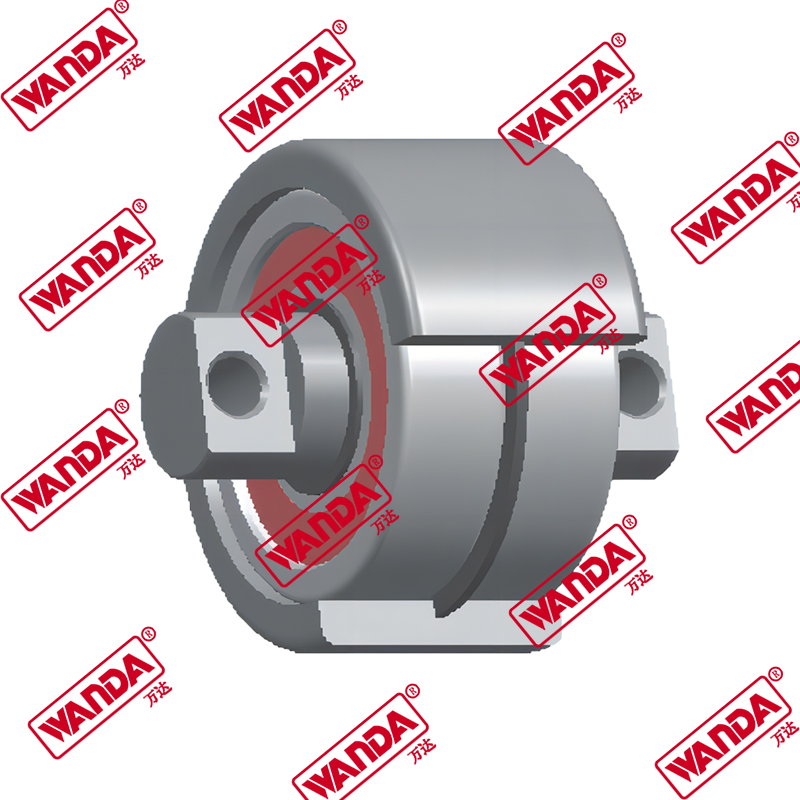
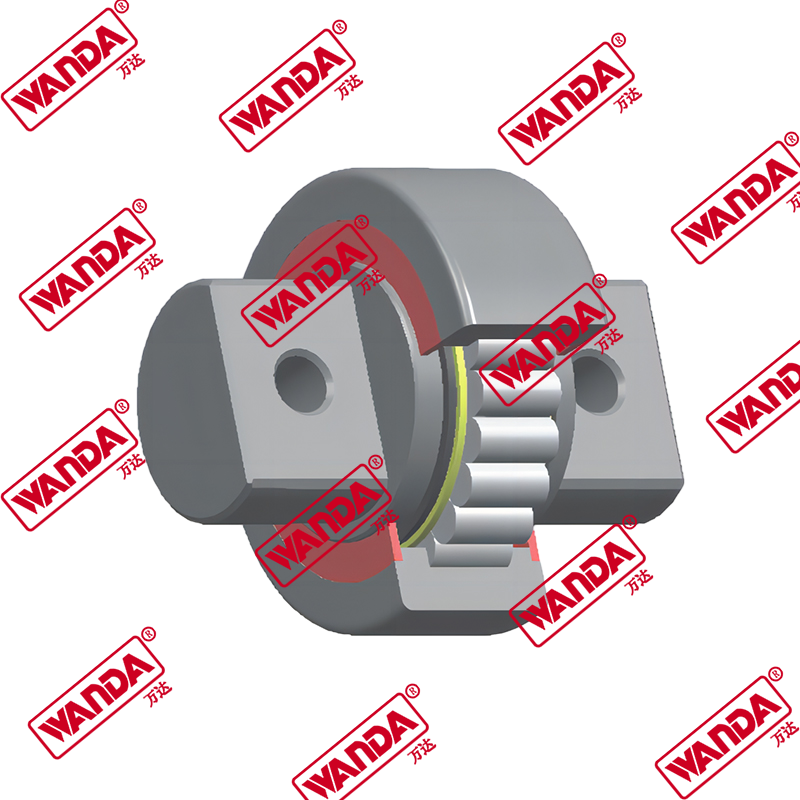
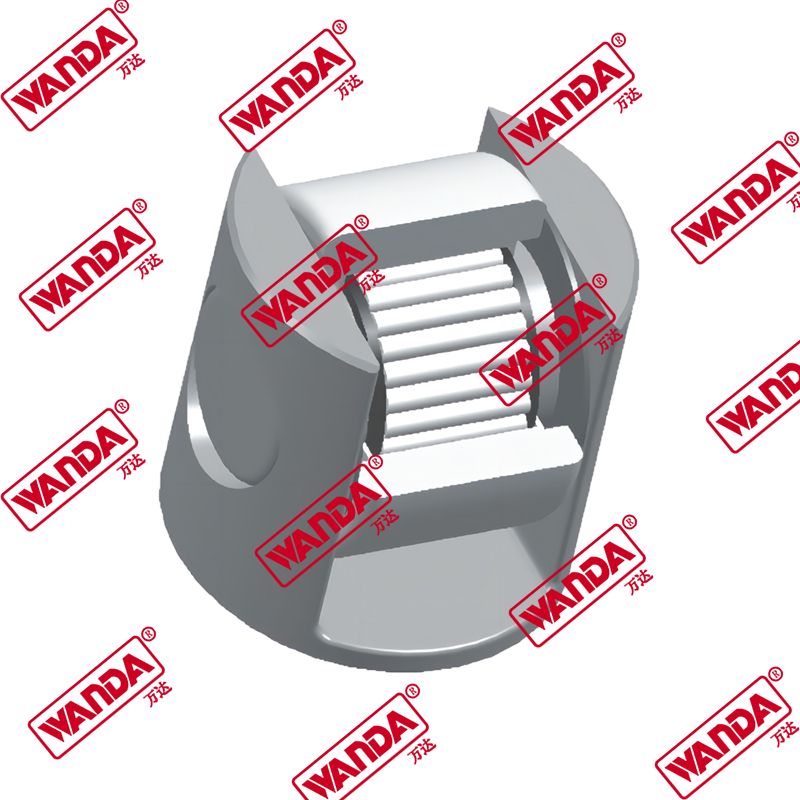
Essential Forklift Spare Parts for Optimal Performance and Longevity
Maintaining a forklift fleet requires in-depth knowledge about the critical components that ensure smooth operations. Forklift spare parts can be categorized into several systems, each with its own maintenance requirements and replacement cycles. Understanding these components is crucial for minimizing downtime and maximizing equipment lifespan.
Complete Breakdown of Critical Forklift Components
The modern forklift consists of numerous interconnected systems, each requiring specific attention:
- Hydraulic System Components:
- Main lift cylinders (single-stage, two-stage, or three-stage designs)
- Tilt cylinders (both forward and backward movement)
- Hydraulic control valves (spool valves, directional control valves)
- Pumps (gear pumps, vane pumps, or piston pumps depending on model)
- Hoses and fittings (high-pressure hydraulic hoses with proper PSI ratings)
- Electrical System Parts:
- Starter motors and alternators (for IC models)
- Wiring harnesses and connectors (weather-resistant varieties)
- Control modules (ECUs for modern forklifts)
- Sensors (pressure, temperature, position sensors)
- Switches and relays (ignition, safety interlock switches)
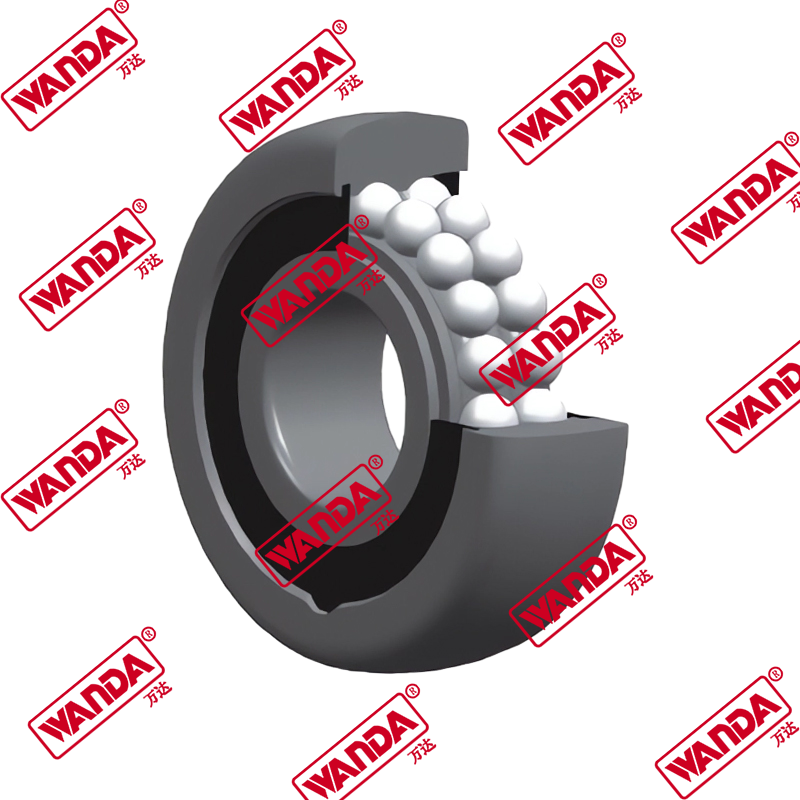
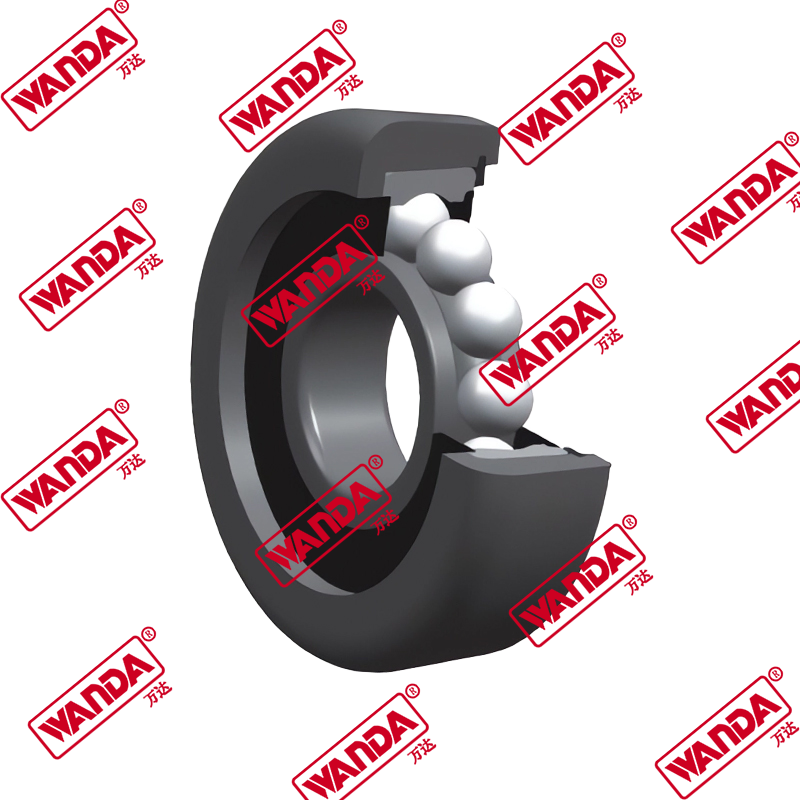
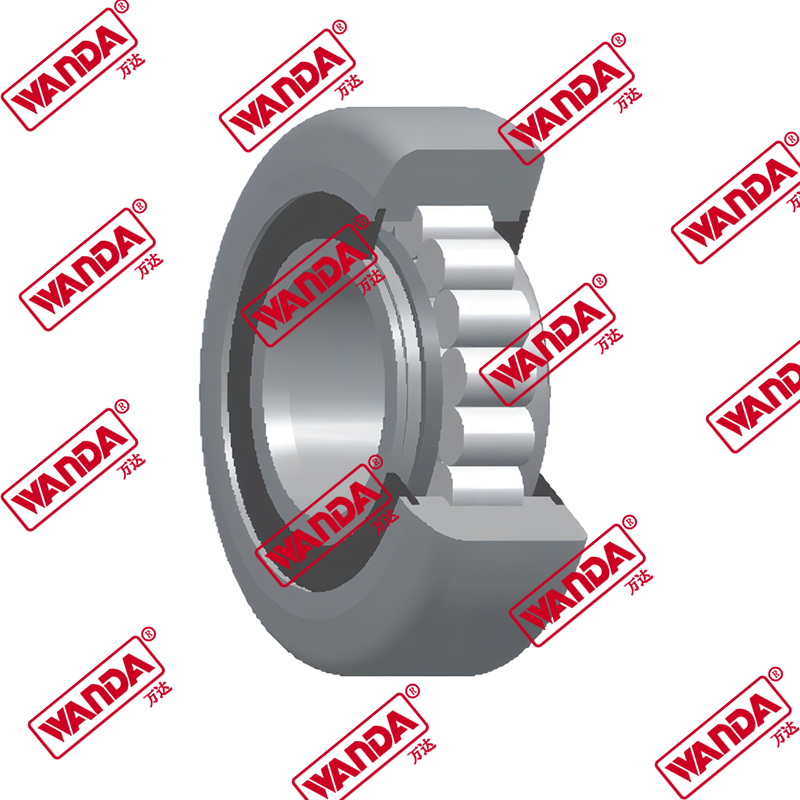
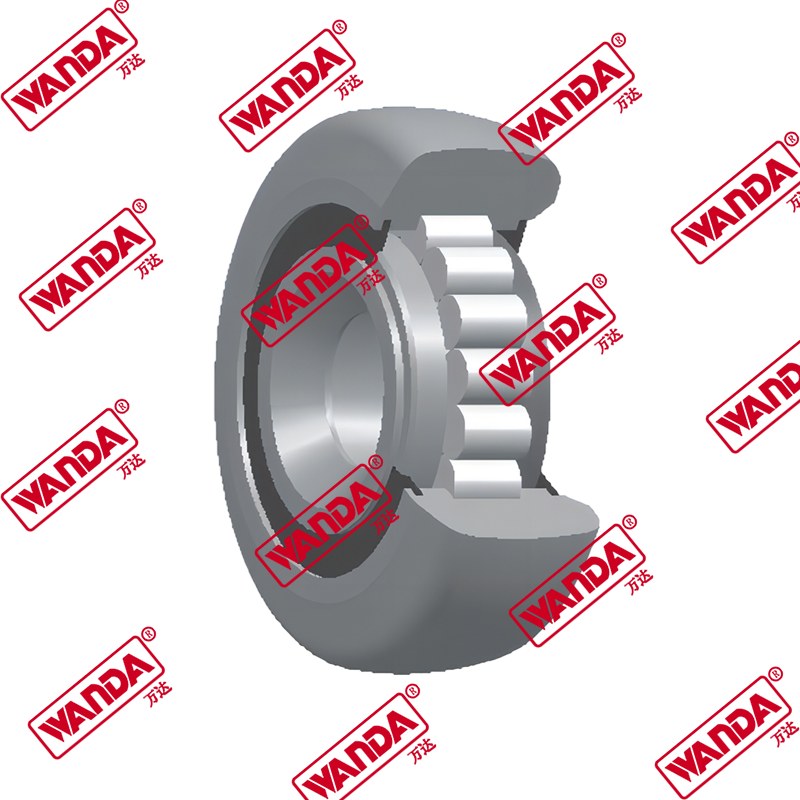
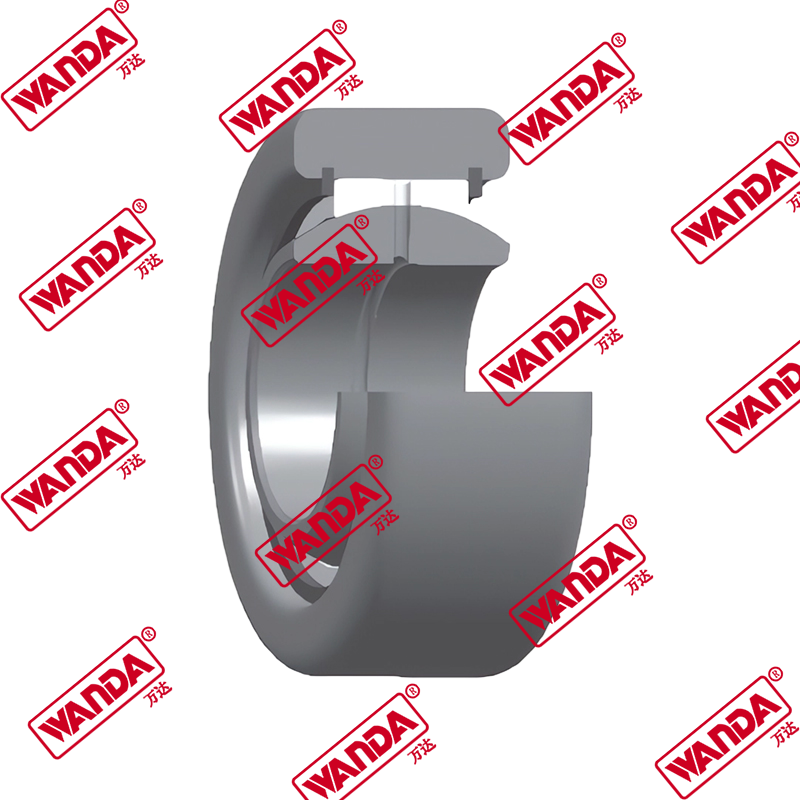
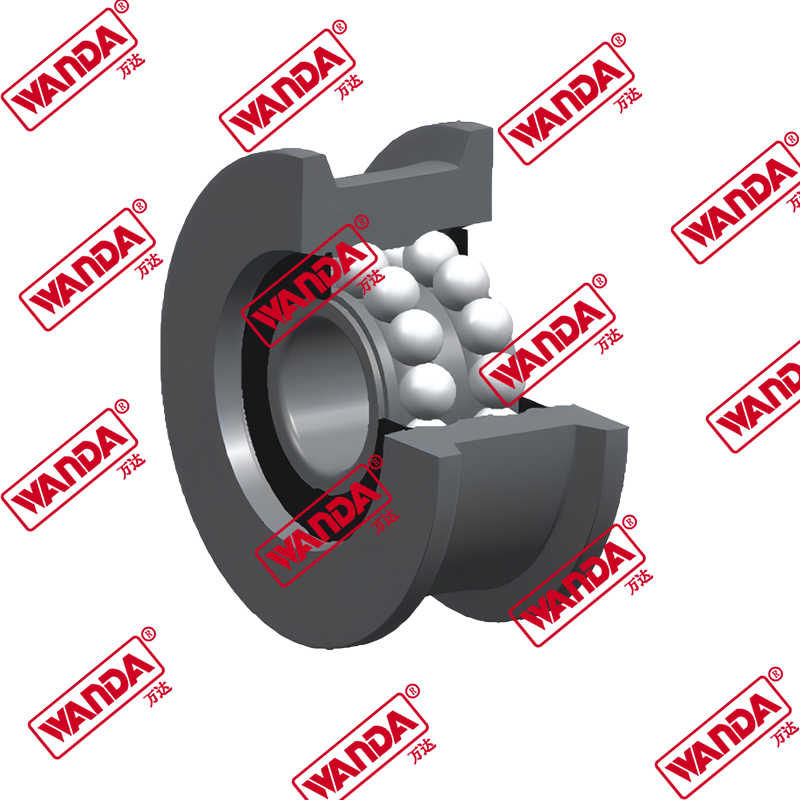
- Mast and Carriage Components:
- Mast rollers and bearings (various sizes for different mast types)
- Side shift cylinders and mechanisms
- Carriage plates and mounting brackets
- Chain anchors and lift chains
Detailed Maintenance Schedule for Critical Parts
| Component | Inspection Frequency | Replacement Indicators | Average Lifespan |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hydraulic Seals | Monthly | Visible leaks, reduced performance | 1-2 years |
| Mast Rollers | Quarterly | Visible wear, unusual noises | 3-5 years |
| Brake Pads | Monthly | Thickness below 1/4", squealing | 6-12 months |
| Electrical Connectors | Bi-annually | Corrosion, intermittent operation | 2-3 years |
| Engine Filters | Per manufacturer spec | Clogging, reduced airflow | 250-500 hours |
Comprehensive Guide to Identifying Genuine Forklift Parts
The difference between genuine forklift parts and counterfeit components can significantly impact your operation's safety and efficiency. This section provides an exhaustive examination of authentication methods.
Multilayered Authentication Process
Verifying part authenticity requires a systematic approach:
- Physical Inspection:
- Surface finish quality (genuine parts have consistent machining marks)
- Weight comparison (counterfeits often use lighter materials)
- Engraving quality (laser-etched vs. stamped markings)
- Packaging Analysis:
- Holographic security labels
- QR code verification systems
- Consistent branding elements
- Proper multilingual documentation
- Performance Verification:
- Precision fit with no modifications required
- Consistent operation without unusual noises
- Expected lifespan matching manufacturer claims
Cost-Benefit Analysis: Genuine vs. Aftermarket
| Factor | Genuine Parts | Aftermarket Parts | Counterfeit Parts |
|---|---|---|---|
| Initial Cost | Highest | 20-40% lower | 50-70% lower |
| Warranty Coverage | Full | Limited | None |
| Failure Rate | 0.5-2% | 3-8% | 15-30% |
| Downtime Impact | Lowest | Moderate | Highest |
| Total Cost of Ownership | Lowest | Moderate | Highest |
Advanced Strategies for Locating Forklift Parts Suppliers Near Me
Finding reliable forklift parts suppliers near me requires a strategic approach that balances multiple factors for optimal parts procurement.
Supplier Evaluation Matrix
Create a weighted scoring system to evaluate potential suppliers:
- Inventory Factors (30% weight):
- Breadth of parts coverage
- Depth of inventory for common parts
- Availability of obsolete parts
- Logistics Factors (25% weight):
- Local warehouse locations
- Emergency delivery options
- Order tracking capabilities
- Technical Factors (25% weight):
- On-staff technicians
- Cross-reference databases
- Troubleshooting support
- Business Factors (20% weight):
- Payment terms
- Return policies
- Contract flexibility
Regional Supplier Network Development
Building a robust local supplier network involves:
- Creating a preferred supplier list with tiered status
- Establishing blanket purchase agreements for common parts
- Developing consignment inventory programs
- Implementing vendor-managed inventory systems
- Setting up cross-training with supplier technical staff
In-Depth Analysis of Forklift Hydraulic Parts Maintenance
Forklift hydraulic parts require specialized knowledge due to their critical role in lifting operations and their complexity.
Hydraulic System Failure Analysis
Common failure modes and their root causes:
| Symptom | Possible Causes | Diagnostic Tests | Corrective Actions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Slow Lifting | Pump wear, valve issues, fluid viscosity | Flow rate test, pressure test | Pump rebuild, fluid change |
| Drifting Load | Cylinder seals, control valve leaks | Drift test, visual inspection | Seal replacement, valve repair |
| Noisy Operation | Cavitation, aeration, component wear | Sound analysis, fluid analysis | Reservoir check, hose inspection |
| Overheating | Restricted flow, excessive pressure | Temperature mapping | Cooler cleaning, relief adjustment |
Preventive Maintenance Program
A comprehensive hydraulic PM program should include:
- Daily Checks:
- Fluid level inspection
- Visual leak detection
- Unusual noise monitoring
- Weekly Tasks:
- Filter condition checks
- Hose and fitting inspections
- Reservoir breather examination
- Monthly Procedures:
- Fluid contamination testing
- Cylinder rod condition checks
- Pump performance testing
- Annual Maintenance:
- Complete fluid replacement
- System flush
- Comprehensive pressure testing
Expert Guide to Forklift Battery Replacement Parts and Maintenance
Proper management of forklift battery replacement parts can extend battery life by 30-40% and significantly reduce operating costs.
Battery Component Failure Analysis
| Component | Failure Symptoms | Testing Methods | Replacement Guidelines |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cells | Reduced capacity, voltage drops | Specific gravity test, load test | Replace if >20% capacity loss |
| Connectors | Heat marks, corrosion | Resistance measurement | Replace when pitting exceeds 30% |
| Cables | Insulation damage, flexibility loss | Visual inspection, continuity test | Replace every 3-5 years |
| Watering System | Overflow, inadequate watering | Flow test, visual inspection | Replace malfunctioning components |
Advanced Battery Maintenance Techniques
Extending battery life requires going beyond basic watering:
- Equalization Charging:
- Procedure frequency based on usage
- Proper voltage settings for battery type
- Temperature compensation requirements
- Load Testing Protocols:
- Standardized test procedures
- Acceptable voltage drop parameters
- Frequency based on battery age
- Cleaning and Neutralization:
- Proper cleaning solutions
- Neutralization of acid spills
- Terminal protection methods
- Storage Procedures:
- Proper charge level for storage
- Temperature-controlled environments
- Maintenance charging schedules
Strategic Parts Management for Fleet Optimization
Implementing advanced parts management strategies can reduce total maintenance costs by 15-25% while improving availability.
Data-Driven Parts Forecasting
Develop predictive models using:
- Historical failure rate data
- Usage patterns by equipment type
- Seasonal demand fluctuations
- Lead time analysis for critical parts
- Component interdependency mapping
Inventory Optimization Models
| Model Type | Best Application | Data Requirements | Implementation Complexity |
|---|---|---|---|
| ABC Analysis | General inventory categorization | Usage frequency, cost data | Low |
| VED Analysis | Criticality assessment | Downtime impact data | Medium |
| FSN Analysis | Movement patterns | Historical issue rates | Medium |
| Simulation Models | Complex fleets | Comprehensive maintenance records | High |